CD14 Monoclonal Antibody (61D3), Super Bright™ 436, eBioscience™
View Cart or Continue shopping.
Description
PRODUCT DETAILS
Host: Mouse
Isotype: IgG1, kappa
Clonality: Monoclonal
Clone: 61D3
Format: Super Bright™ 436
Reactivity: Human
Application: Flow Cytometry
Tested Dilution: 5 µL (0.5 µg)/test
Concentration: 5 µL/Test
Storage: 4° C, store in dark, DO NOT FREEZE!
Formulation: PBS, pH 7.2, containing 0.09% sodium azide
Purification: Affinity chromatography
Data Sheet: TDS
Specific Information
Description: The 61D3 monoclonal antibody reacts with human CD14, a 53-55 kDa GPI-linked glycoprotein. CD14 is expressed on monocytes, interfollicular macrophages and some dendritic cells. Complexes of LPS and LBP (LPS-Binding Protein) bind with high affinity to monocytes through the surface CD14.
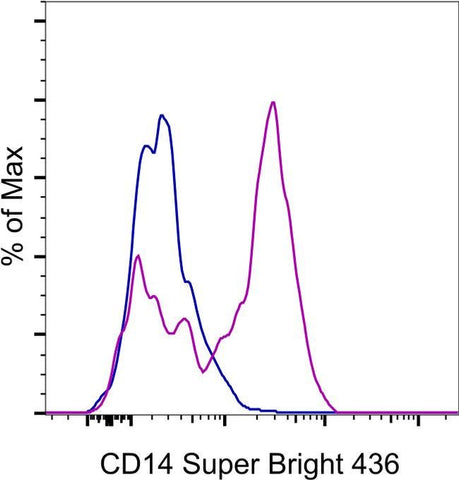
Applications Reported: This 61D3 antibody has been reported for use in flow cytometric analysis.
Applications Tested: This 61D3 antibody has been pre-diluted and tested by flow cytometric analysis of normal human peripheral blood cells. This may be used at 5 µL (0.5 µg) per test. A test is defined as the amount (µg) of antibody that will stain a cell sample in a final volume of 100 µL. Cell number should be determined empirically but can range from 10^5 to 10^8 cells/test.
Super Bright 436 can be excited with the violet laser line (405 nm) and emits at 436 nm. We recommend using a 450/50 bandpass filter, or equivalent. Please make sure that your instrument is capable of detecting this fluorochrome.
When using two or more Super Bright dye-conjugated antibodies in a staining panel, it is recommended to use Super Bright Complete Staining Buffer (Product # SB-4401) to minimize any non-specific polymer interactions. Please refer to the datasheet for Super Bright Staining Buffer for more information.
Excitation: 405 nm; Emission: 436 nm; Laser: Violet Laser
Super Bright Polymer Dyes are sold under license from Becton, Dickinson and Company.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Not for resale without express authorization.
