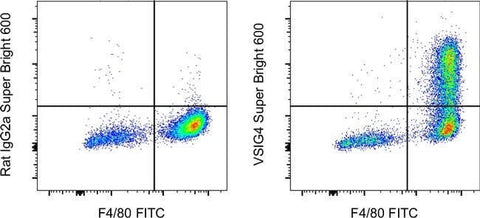
VSIG4 Monoclonal Antibody (NLA14), Super Bright™ 600, eBioscience™
カートを見る または ショッピングを続ける
説明
PRODUCT DETAILS
Host: Rat
Isotype: IgG2a, kappa
Clonality: Monoclonal
Clone: NLA14
Format: Super Bright™ 600
Reactivity: Mouse
Application: Flow Cytometry
Tested Dilution: 1.0 µg/test
Concentration: 0.2 mg/mL
Storage: 4° C, store in dark, DO NOT FREEZE!
Formulation: PBS, pH 7.2, containing 0.09% sodium azide
Purification: Affinity chromatography
Data Sheet: TDS
Specific Information
Description: This NLA14 monoclonal antibody recognizes mouse V-Set and Immunoglobulin domain containing 4 (VSIG4), also known as Complement Receptor of the Immunoglobulin superfamily (CRIg) or Z39Ig. VSIG4 is a type I transmembrane glycoprotein structurally related to the B7 family of immune regulatory proteins. It contains one complete V-type Ig domain and one truncated C-type Ig domain. VSIG4 is exclusively expressed on tissue resident and tumor infiltrating macrophages. It has been shown to bind complement components C3b and iC3b. This binding inhibits the alternative complement pathway and facilitates phagocytosis of complement-opsonized pathogens. VSIG4 has also been reported to suppress T cell activation, proliferation and IL-2 production thereby playing a role in the maintenance of peripheral T cell tolerance and suppression of established inflammation. Expression of VSIG4 on tumor-infiltrating macrophages suggests its role in immune evasion. Pro-inflammatory stimuli such as TNF and LPS have been reported to down-regulate the expression of VSIG4. Peritoneal macrophages in Balb/c mice express significantly higher levels of VSIG4 than such macrophages in C57Bl/6 or Swiss Webster mice.
The NLA14 antibody will recognize VSIG4 on cells that have been formaldehyde-fixed and permeabilized. This antibody does not block the ligation of VSIG4 to its T cell ligand. The NLA14 antibody does not cross-react with rat or human VSIG4.
Applications Reported: This NLA14 antibody has been reported for use in flow cytometric analysis.
Applications Tested: This NLA14 antibody has been tested by flow cytometric analysis of mouse peritoneal exudate cells. This may be used at less than or equal to 1.0 µg per test. A test is defined as the amount (µg) of antibody that will stain a cell sample in a final volume of 100 µL. Cell number should be determined empirically but can range from 10^5 to 10^8 cells/test. It is recommended that the antibody be carefully titrated for optimal performance in the assay of interest.
Super Bright 600 is a tandem dye that can be excited with the violet laser line (405 nm) and emits at 600 nm. We recommend using a 610/20 bandpass filter. Please make sure that your instrument is capable of detecting this fluorochrome.
When using two or more Super Bright dye-conjugated antibodies in a staining panel, it is recommended to use Super Bright Complete Staining Buffer (Product # SB-4401) to minimize any non-specific polymer interactions. Please refer to the datasheet for Super Bright Staining Buffer for more information.
Light sensitivity: This tandem dye is sensitive to photo-induced oxidation. Please protect this vial and stained samples from light.
Fixation: Samples can be stored in IC Fixation Buffer (Product # 00-8222-49) (100 µL of cell sample + 100 µL of IC Fixation Buffer) or 1-step Fix/Lyse Solution (Product # 00-5333-57) for up to 3 days in the dark at 4°C with minimal impact on brightness and FRET efficiency/compensation. Some generalizations regarding fluorophore performance after fixation can be made, but clone specific performance should be determined empirically.
Excitation: 405 nm; Emission: 600 nm; Laser: Violet Laser
Super Bright Polymer Dyes are sold under license from Becton, Dickinson and Company.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Not for resale without express authorization.
